Arteriogram
Arteriogram or arteriography involves injection of contrast material into one of the arteries so as to get X ray image of the blood vessel to determine narrowing of arteries. An arteriogram is also called an angiogram.This diagnostic test is used to detect vascular conditions like aneurysm, stenosis or blockage.
Angiograms can be specific to the blood vessels that are being examined, such as cerebral Angiography, renal angiography, aortography or Cardiac Catheterization. Coronary Angiogram or Catheter Angiogram is a minimally invasive procedure where a catheter is inserted into one of the arteries or veins. An IV line is inserted into a blood vessel of either the arm, neck or chest. A catheter is inserted though the IV and contrast material is injected into the desired vein or artery that has to be viewed. A series of x-rays are taken. The contrast material in the blood vessels causes them to appear opaque on an x-ray. There is a small risk of arteriogram leading to blood clots or bleeding and infection at the IV site.
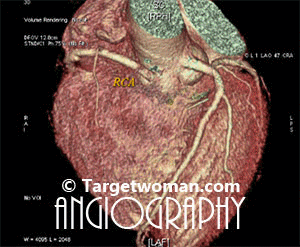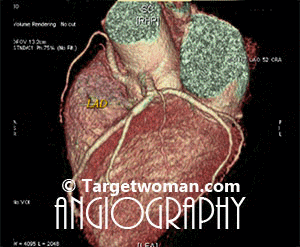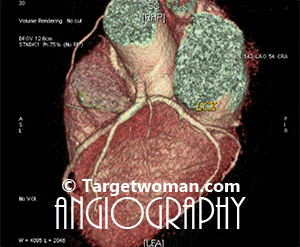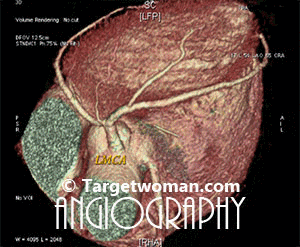
Non invasive 64 slice CT (Computed Tomography) Angiogram (64 MSCTA) can identify the presence of early atherosclerotic plaque deposition before it shows up in the conventional catheter angiogram. Multi slice CT Angiogram can differentiate between various types of plaques - calcified, soft or mixed type. CTA of the multi slice scanners allows faster and comprehensive assessment of arterial blocks and is an important tool in the evaluation of stroke patients - as it enables effective diagnosis of cervicocranial vascular pathologies such as carotid artery stenosis. A 64 slice CT scan images may be pieced together to reveal 3 D images for extracting additional information.
Cyanosis
Cyanosis is the condition where the skin of a person turns blue or purplish due to reduced oxygen. This bluish color is noticed mostly on the lips, fingers and toes. It is the result of circulatory or heart problems. It is indicative of too little oxygen in the blood. Cyanosistic heart disease is characterised by bluish or grayish skin, tiredness and puffy eyes. Chest pain and fainting might occur.
Causes of cyanosis
- Arterial obstruction
- Chemical exposure
- Congenital heart disease
- Exposure to extreme cold
- Arteriosclerosis
- COPD
- Cystic Fibrosis
- Pneumonia
- DVT
- Raynaud's Disease
- Asthma
Diagnostic tests such as chest x-ray, complete blood count, ECG, Heart MRI, Cardiac catherization and pulse oximeter might be done to ascertain the problem leading to cyanosis. Some congenital heart diseases might need surgery to rectify any birth defect.
Cardiomyopathy
Cardiomyopathy refers to deteriorated functioning of the heart muscles. This happens due to thickened or enlarged heart muscles. It is a term that includes many conditions that occur due to damage to the heart ventricles. It can also be indicative of heart failure, arrhythmia and systemic embolization. The symptoms of cardiomyopathy are typical of most heart ailments - shortness of breath, fainting, palpitations, fatigue and chest pain. Swelling may develop in the feet and legs. Fluid might build up in the lungs and abdomen.
ECG will show abnormal results. MRI is often resorted to. Cardiac Catherization might be done to measure pressure in the heart. In most cases, Cardiomyopathy cannot usually be completely cured. Treatment can ease symptoms.
Tags: #Arteriogram #Cyanosis #CardiomyopathyAt TargetWoman, every page you read is crafted by a team of highly qualified experts — not generated by artificial intelligence. We believe in thoughtful, human-written content backed by research, insight, and empathy. Our use of AI is limited to semantic understanding, helping us better connect ideas, organize knowledge, and enhance user experience — never to replace the human voice that defines our work. Our Natural Language Navigational engine knows that words form only the outer superficial layer. The real meaning of the words are deduced from the collection of words, their proximity to each other and the context.
Diseases, Symptoms, Tests and Treatment arranged in alphabetical order:

A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W X Y Z
Bibliography / Reference
Collection of Pages - Last revised Date: February 23, 2026



